publications
Publications in reverse chronological order.
See my Google Scholar page for more details.
2017
-
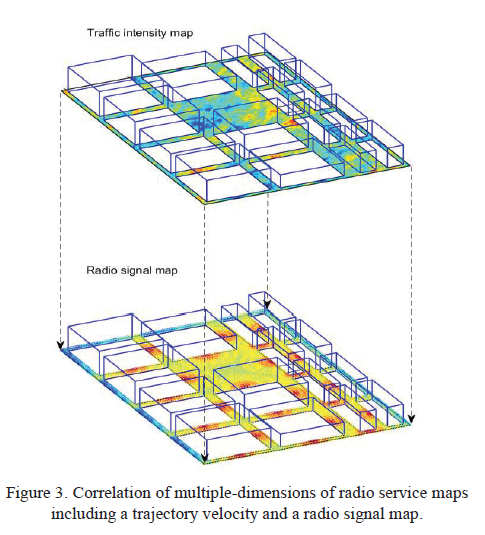 Multi-dimensional radio service maps for position-based self-organized networksPer Tengkvist , George P Koudouridis , Christer Qvarfordt , and 2 more authorsIn 2017 IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD) , 2017
Multi-dimensional radio service maps for position-based self-organized networksPer Tengkvist , George P Koudouridis , Christer Qvarfordt , and 2 more authorsIn 2017 IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD) , 2017Increasing spectral and energy efficiency in future networks requires flexible and timely allocation of radio resources along multiple dimensions including frequency, time and space. Although this multi-dimensionality offers additional degrees of freedom, it however comes at the cost of higher complexity. To this end, it is envisaged that spatial information associated with user resource allocation will provide a means for an efficient utilization of a dense radio access network (RAN) infrastructure in a proactive and self-optimized manner. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that aims at the utilization of multi-dimensional (MD) radio service maps (RSM) for storing and exploiting position-based information. Requirements, key concepts and functions are described. The potential gains in energy consumption and efficiency of the radio service maps are shown by means of numerical results for an ultra-dense network deployment scenario.
@inproceedings{tengkvist2017multi, title = {Multi-dimensional radio service maps for position-based self-organized networks}, author = {Tengkvist, Per and Koudouridis, George P and Qvarfordt, Christer and Dryjanski, Marcin and Cellier, Malek}, booktitle = {2017 IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2017}, organization = {IEEE}, }
2010
-
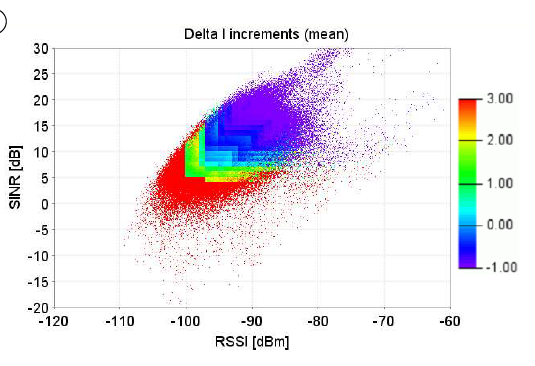 Enhancing uplink performance in UTRAN LTE networks by load adaptive power controlRobert Müllner , Carsten F Ball , Malek Boussif , and 5 more authorsEuropean transactions on telecommunications, 2010
Enhancing uplink performance in UTRAN LTE networks by load adaptive power controlRobert Müllner , Carsten F Ball , Malek Boussif , and 5 more authorsEuropean transactions on telecommunications, 2010Uplink power control in 3GPP UTRAN long term evolution (LTE) networks consists of a closed-loop scheme around an open-loop point of operation. The uplink performance of the network is decisively influenced by power control. This paper provides insight into the uplink power control procedure and its interworking with adaptive transmission bandwidth (ATB) as well as adaptive modulation and coding (AMC). A detailed performance evaluation is presented based on system level simulations. In the first step, the performance of pure open-loop power control (OLPC) was analysed and the impact of parameter settings on resource allocation, utilisation of specific modulation and coding schemes (MCS), re-transmission rate, and resulting throughput was determined. A two-dimensional parameter optimisation for full path-loss (PL) compensation and fractional power control (FPC) was performed to conclude the best strategy for the trade-off between network capacity and coverage. In the second step, the impact of traffic load on the interaction between the different LTE radio resource management algorithms was analysed. A novel strategy is presented which introduces traffic load dependent decisions for the closed-loop power control (CLPC) component to optimise the uplink throughput. This solution provides an automatic configuration for LTE networks without further intervention by the operator.
@article{mullner2010enhancing, title = {Enhancing uplink performance in UTRAN LTE networks by load adaptive power control}, author = {M{\"u}llner, Robert and Ball, Carsten F and Boussif, Malek and Lienhart, Johann and Hric, Peter and Winkler, Hubert and Kremnitzer, Kurt and Kronlachner, Rudolf}, journal = {European transactions on telecommunications}, volume = {21}, number = {5}, pages = {458--468}, year = {2010}, publisher = {Wiley Online Library}, } -
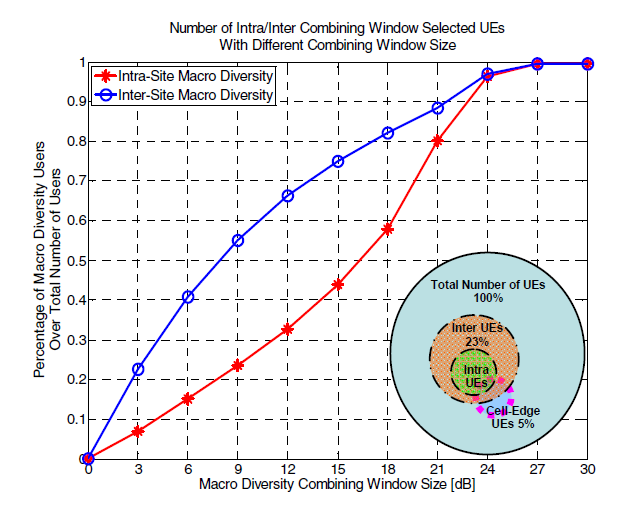 Uplink coordinated multi-point for LTE-A in the form of macro-scopic combiningZheng Naizheng , Malek Boussif , Claudio Rosa , and 4 more authorsIn 2010 IEEE 71st Vehicular Technology Conference , 2010
Uplink coordinated multi-point for LTE-A in the form of macro-scopic combiningZheng Naizheng , Malek Boussif , Claudio Rosa , and 4 more authorsIn 2010 IEEE 71st Vehicular Technology Conference , 2010For the future LTE-Advanced network, one of the requirements in the uplink (UL) direction is to enhance the celledge user performances. Coordinated multi-point reception in the UL is one of the techniques being investigated to further improve the performance of LTE networks. With the help of the information coordination through the links between the sites and advanced receivers the UL performance can be improved. The simulation results show that, with the ideal interference cancellation, inter-Site maximum ratio combining, and optimized closed-loop and open-loop fractional power control, there are about 27% gains for the 5% outage user throughput and 12% gains for the average user throughput. As shown in this paper, these gains from UL macro-scopic multi-cell combining between sites are achieved for optimized power control, ideal interference cancellation receivers, and X2 with no delay and high bandwidth.
@inproceedings{naizheng2010uplink, title = {Uplink coordinated multi-point for LTE-A in the form of macro-scopic combining}, author = {Naizheng, Zheng and Boussif, Malek and Rosa, Claudio and Kovacs, Istvan Z and Pedersen, Klaus I and Wigard, Jeroen and Mogensen, Preben E}, booktitle = {2010 IEEE 71st Vehicular Technology Conference}, pages = {1--5}, year = {2010}, organization = {IEEE}, } -
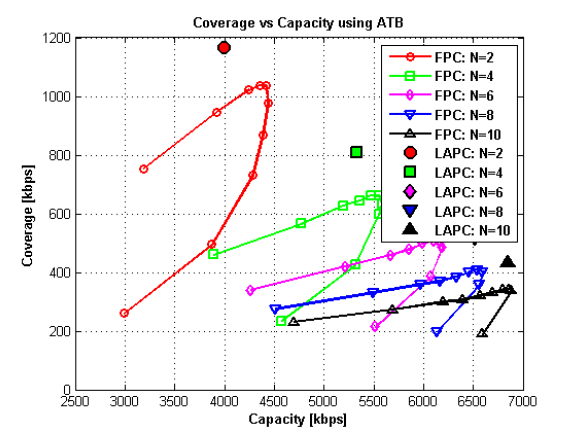 Load adaptive power control in LTE UplinkMalek Boussif , Claudio Rosa , Jeroen Wigard , and 1 more authorIn 2010 European Wireless Conference (EW) , 2010
Load adaptive power control in LTE UplinkMalek Boussif , Claudio Rosa , Jeroen Wigard , and 1 more authorIn 2010 European Wireless Conference (EW) , 2010In LTE Uplink, the slow varying pathgain and shadowing are compensated by the standardized open loop power control (OLPC) which is based on a power density offset and a compensating factor for the pathloss experienced by the users. The optimization of those parameters reveals a dependency on the allocated bandwidth. A Load Adaptive Power Control (LAPC) algorithm is proposed to handle the bandwidth variations and ensure optimal system performance. In this contribution it is shown that using closed loop power control commands to adapt the transmission power density to the used bandwidth, it is possible to achieve coverage gains up to 60% while maintaining a cell throughput comparable to the reference case.
@inproceedings{boussif2010load, title = {Load adaptive power control in LTE Uplink}, author = {Boussif, Malek and Rosa, Claudio and Wigard, Jeroen and M{\"u}llner, Robert}, booktitle = {2010 European Wireless Conference (EW)}, pages = {288--293}, year = {2010}, organization = {IEEE}, }
2009
-
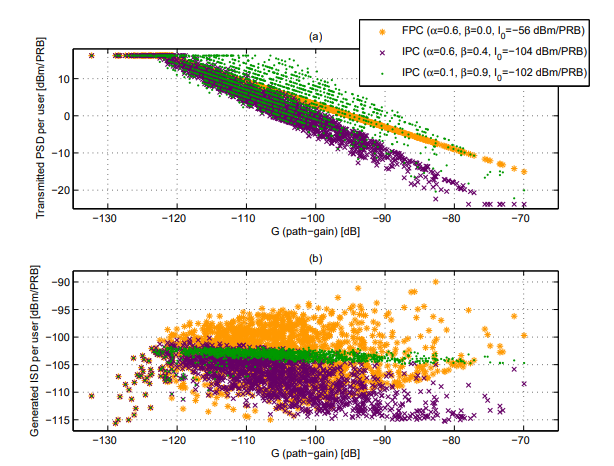 Scheduling and Link Adaptation for Uplink SC-FDMA Systems-A LTE Case StudyFrancesco Davide Calabrese2009
Scheduling and Link Adaptation for Uplink SC-FDMA Systems-A LTE Case StudyFrancesco Davide Calabrese2009ong Term Evolution (LTE) is a beyond 3G system conceived with the objective of providing substantial advances in terms of data rates, Quality of Service (QoS) provisioning and cost reduction for users and operators with respect to currently available 3G systems. This project focuses on a subset of Radio Resource Management (RRM) functionalities within the context of LTE uplink and specifically on Power Control (PC), Adaptive Transmission Bandwidth (ATB) and Packet Scheduler (PS). PC and ATB are link adaptation techniques whose role is to adapt the power and transmission bandwidth to the time-varying nature of the channel. The PS entity, instead, multiplexes users in time and frequency domain based on a large variety of parameters like channel conditions and QoS requirements. In a LTE system the orthogonality of users within the same cell, realized via the Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) scheme, eliminates the intra-cell interference leaving the PC functionality with the task of limiting the inter-cell interference - due to a frequency reuse factor of one - and the terminal power consumption. A PC algorithm therefore is proposed which, compared to the open-loop form of the standardized PC formula, introduces the dependency from the user generated interference when setting the transmitting power. The results show a considerable performance gain that can be used to improve the outage user throughput (by more than 50%) or the cell capacity (by more than 15%) by proper parameter tuning. Such performance boost is preserved only in a full (infinite) buffer traffic whereas a finite buffer traffic scenario considerably reduces the gain due to the different distribution of users in the cell and consequently the different interference patterns. The main contribution of this research project pertains the design of the PS entity. In LTE uplink the adoption of the Single Carrier - Frequency Domain Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) scheme limits the flexibility of the allocation schemes. The problem is initially bypassed by designing a simple scheduler which assumes a Fixed Transmission Bandwidth (FTB). This gives the possibility to quantify the frequency selectivity and multi-user diversity gains obtained from a channel-aware approach compared to a channel-blind one. In a second phase a scheduling algorithm (novel to the knowledge of the author) is designed to integrate the flexibility of ATB into the scheduler. Such algorithm is shown throughout the thesis to provide flexibility in terms of inbuilt adaptation to cell load, user power limitations and QoS requirements when driven by appropriate scheduling metrics. Moreover the comparison of FTB- and ATB-based schedulers reveals interesting viewpoints regarding the principles of multi-user diversity gain. In the last part of the thesis the design of the scheduling framework is completed by the addition of a time domain unit motivated by control channel limitations, computational complexity and QoS requirements like Guaranteed Bit Rate (GBR). The focus is therefore shifted on the design of time and frequency domain metrics which are modified as to take into account additional requirements, e.g. the GBR, and different traffic types, e.g. the mix of Constant Bit Rate (CBR) and Best Effort (BE) traffics. The proposed metrics are shown to effectively prioritize the users based on their traffic type and GBR requirement while keeping a similar cell throughput performance.
@book{calabrese2009scheduling, title = {Scheduling and Link Adaptation for Uplink SC-FDMA Systems-A LTE Case Study}, author = {Calabrese, Francesco Davide}, year = {2009}, isbn = {978-87-92328-20-5}, chapter = {3}, publisher = {Aalborg Universitet}, }
2008
-
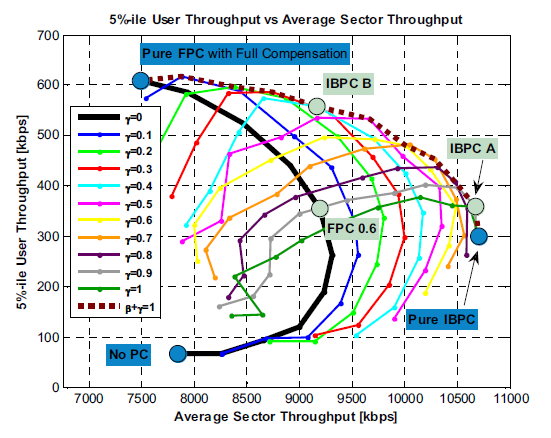 Interference based power control performance in LTE uplinkMalek Boussif , Nestor Quintero , Francesco D Calabrese , and 2 more authorsIn 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems , 2008
Interference based power control performance in LTE uplinkMalek Boussif , Nestor Quintero , Francesco D Calabrese , and 2 more authorsIn 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems , 2008In LTE uplink, the slow varying path gain and shadowing are compensated by the standardized open loop power control (OLPC). Further optimization of the system performance can be done via closed loop power control commands. In this contribution, it is shown that using such commands to control the interference caused by users to the system, it is possible to achieve a gain in the order of 20% on the average cell throughput while maintaining the same outage cell throughput compared to the performance of the OLPC. Furthermore, gain on both average and outage cell throughput can be achieved by tuning the parameters of the proposed scheme.
@inproceedings{boussif2008interference, title = {Interference based power control performance in LTE uplink}, author = {Boussif, Malek and Quintero, Nestor and Calabrese, Francesco D and Rosa, Claudio and Wigard, Jeroen}, booktitle = {2008 IEEE International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems}, pages = {698--702}, year = {2008}, organization = {IEEE}, }
2007
-
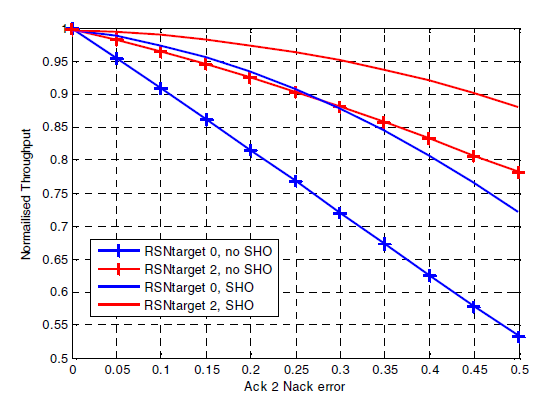 Errors on the HSUPA E-HICH channel and their effect on System PerformanceMalek Boussif , Jeroen Wigard , Troels E Kolding , and 1 more authorIn 2007 IEEE 65th Vehicular Technology Conference-VTC2007-Spring , 2007
Errors on the HSUPA E-HICH channel and their effect on System PerformanceMalek Boussif , Jeroen Wigard , Troels E Kolding , and 1 more authorIn 2007 IEEE 65th Vehicular Technology Conference-VTC2007-Spring , 2007The E-HICH is a downlink control channel associated to the HARQ procedure in HSUPA. It allows the MAC-e entity in the NodeB to signal the correct or incorrect reception of a given MAC-e PDU by transmitting ACKs or NACKs. Errors on this channel can cause misinterpretations and impact the overall system performance. This paper looks at the performance impact caused by two types of errors: ACK misinterpreted as NACK and vice versa. Detailed user and system performance results versus the error levels on the E-HICH are provided for both cases. A2N errors cause a direct degradation of the user throughput that increases with the probability. N2A errors have a more intricate impact that leads to opposite effects. On the one hand, it causes the level of RLC retransmissions to increase. On the other hand, the missing PDUs change the HARQ operating point which will then decrease the RLC retransmission level. The overall consequence is a lowered cell and user throughput for lowly loaded networks, whereas it is almost imperceptible in fully loaded networks.
@inproceedings{boussif2007errors, title = {Errors on the HSUPA E-HICH channel and their effect on System Performance}, author = {Boussif, Malek and Wigard, Jeroen and Kolding, Troels E and Madsen, Nina A}, booktitle = {2007 IEEE 65th Vehicular Technology Conference-VTC2007-Spring}, pages = {949--953}, year = {2007}, organization = {IEEE}, }
2006
-
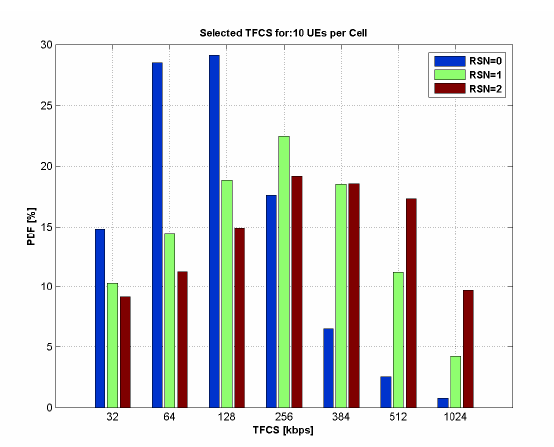 High Speed Uplink Packet Access evaluation by dynamic network simulationsJeroen Wigard , Malek Boussif , NH Madsen , and 3 more authorsIn 2006 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications , 2006
High Speed Uplink Packet Access evaluation by dynamic network simulationsJeroen Wigard , Malek Boussif , NH Madsen , and 3 more authorsIn 2006 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications , 2006High speed uplink packet access (HSUPA) improves the cell throughput by faster scheduling, L1 HARQ and enhanced bit rates. This paper introduces a dynamic system simulator for studying HSUPA system performance. This simulator is used to analyze the effect on the cell throughput of increasing the BLER target and the target number of transmissions. The L3 cell throughput increases when the target number of transmissions increases, while the control overhead in terms of transmission power is estimated to be approximately 25%
@inproceedings{wigard2006high, title = {High Speed Uplink Packet Access evaluation by dynamic network simulations}, author = {Wigard, Jeroen and Boussif, Malek and Madsen, NH and Brix, Mads and Corneliussen, S and Laursen, EA}, booktitle = {2006 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications}, pages = {1--5}, year = {2006}, organization = {IEEE}, }
2005
-
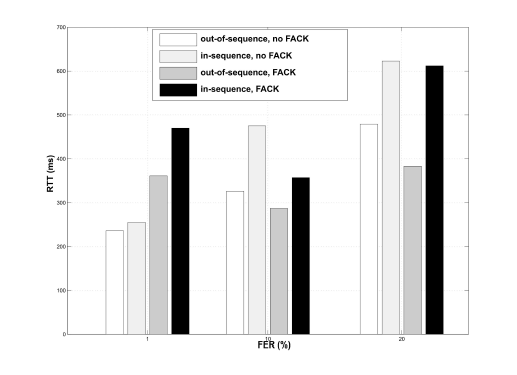 The impact of RLC delivery sequence on FTP performance in UMTSOumer Teyeb , Malek Boussif , T Sorensen , and 2 more authorsIn The Eigth International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC05) , 2005
The impact of RLC delivery sequence on FTP performance in UMTSOumer Teyeb , Malek Boussif , T Sorensen , and 2 more authorsIn The Eigth International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC05) , 2005The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol of Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS) provides an option for in- or out-of-sequence delivery of Service Data Units (SDUs) to upper layers. In this paper, the impact of this setting on the performance of File Transport Protocol (FTP) sessions is investigated. The investigations are carried out using a real-time emulation platform, and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) with and without Selective Acknowledgement/Forward Acknowledgment (SACK/FACK) options. The results show that out-of-sequence delivery has a negative impact at higher bandwidths and TCP FACK exacerbates the problem. This is mainly due to the aggressive retransmission strategy employed by FACK, which considers the gaps in a SACK report caused by reordering as lost segments and retransmits them immediately.
@inproceedings{teyeb2005impact, title = {The impact of RLC delivery sequence on FTP performance in UMTS}, author = {Teyeb, Oumer and Boussif, Malek and Sorensen, T and Wigard, Jeroen and Mogensen, P}, booktitle = {The Eigth International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC05)}, year = {2005}, } -
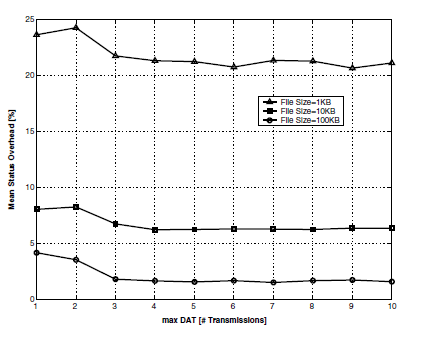 Emulation based performance investigation of FTP file downloads over UMTS dedicated channelsOumer M Teyeb , Malek Boussif , Troels B Sørensen , and 2 more authorsIn International Conference on Networking , 2005
Emulation based performance investigation of FTP file downloads over UMTS dedicated channelsOumer M Teyeb , Malek Boussif , Troels B Sørensen , and 2 more authorsIn International Conference on Networking , 2005The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol of Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS) provides a link layer reliability that could mitigate the effects of the hostile radio propagation channel on packet data transmission. The RLC standard provides several mechanisms and associated parameters that determine the workings of this reliability scheme. In this paper, the impact of some of these schemes and parameters on the performance of FTP file downloads is investigated. The investigations are carried out using a real time emulation platform, which makes the results from this study more realistic than simulation or simplified analytical studies as the overall End-2-End performance is analyzed involving real world protocol implementations.
@inproceedings{teyeb2005emulation, title = {Emulation based performance investigation of FTP file downloads over UMTS dedicated channels}, author = {Teyeb, Oumer M and Boussif, Malek and S{\o}rensen, Troels B and Wigard, Jeroen and Mogensen, Preben E}, booktitle = {International Conference on Networking}, pages = {388--396}, year = {2005}, organization = {Springer}, } -
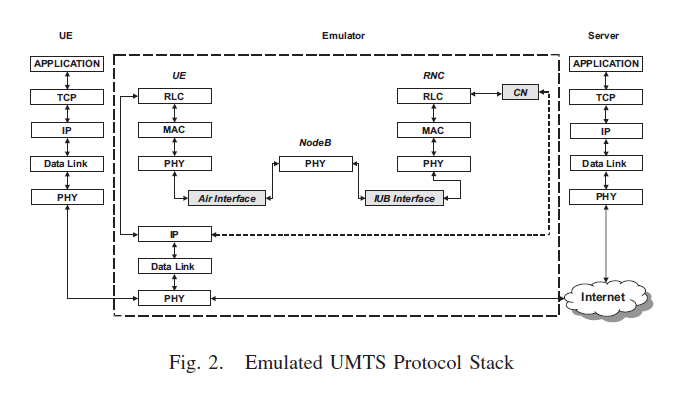 RESPECT: A Real-time Emulator for Service Performance Evaluation in Cellular neTworksOumer Teyeb , Malek Boussif , Troels Bundgaard Sørensen , and 2 more authorsIn 62nd IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference , 2005
RESPECT: A Real-time Emulator for Service Performance Evaluation in Cellular neTworksOumer Teyeb , Malek Boussif , Troels Bundgaard Sørensen , and 2 more authorsIn 62nd IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference , 2005The evaluation and optimization of packet service performance in wireless networks is a complex process, considering the number of heterogeneous entities and protocols that are involved. An emulation platform comes at hand for such performance investigations as it provides a means to see the performance from an end-2-end (E2E), user-perceived Quality Of Service (QoS) point of view. In this paper, the design and implementation of RESPECT, an easily configurable network emulator is described. RESPECT was originally geared towards Universal Mobile Communications System (UMTS) networks, but thanks to its modular and scalable design, it is being extended for generic heterogeneous networks. Using RESPECT, QoS studies can be carried out to study the behavior of different services in different network conditions, identify generalized service dependent performance metrics for already existing services and predict network environment requirements for future services.
@inproceedings{teyeb2005respect, title = {RESPECT: A Real-time Emulator for Service Performance Evaluation in Cellular neTworks}, author = {Teyeb, Oumer and Boussif, Malek and S{\o}rensen, Troels Bundgaard and Mogensen, Preben Elgaard and Wigard, Jeroen}, booktitle = {62nd IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference}, year = {2005}, organization = {Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Communications and Information~…}, }